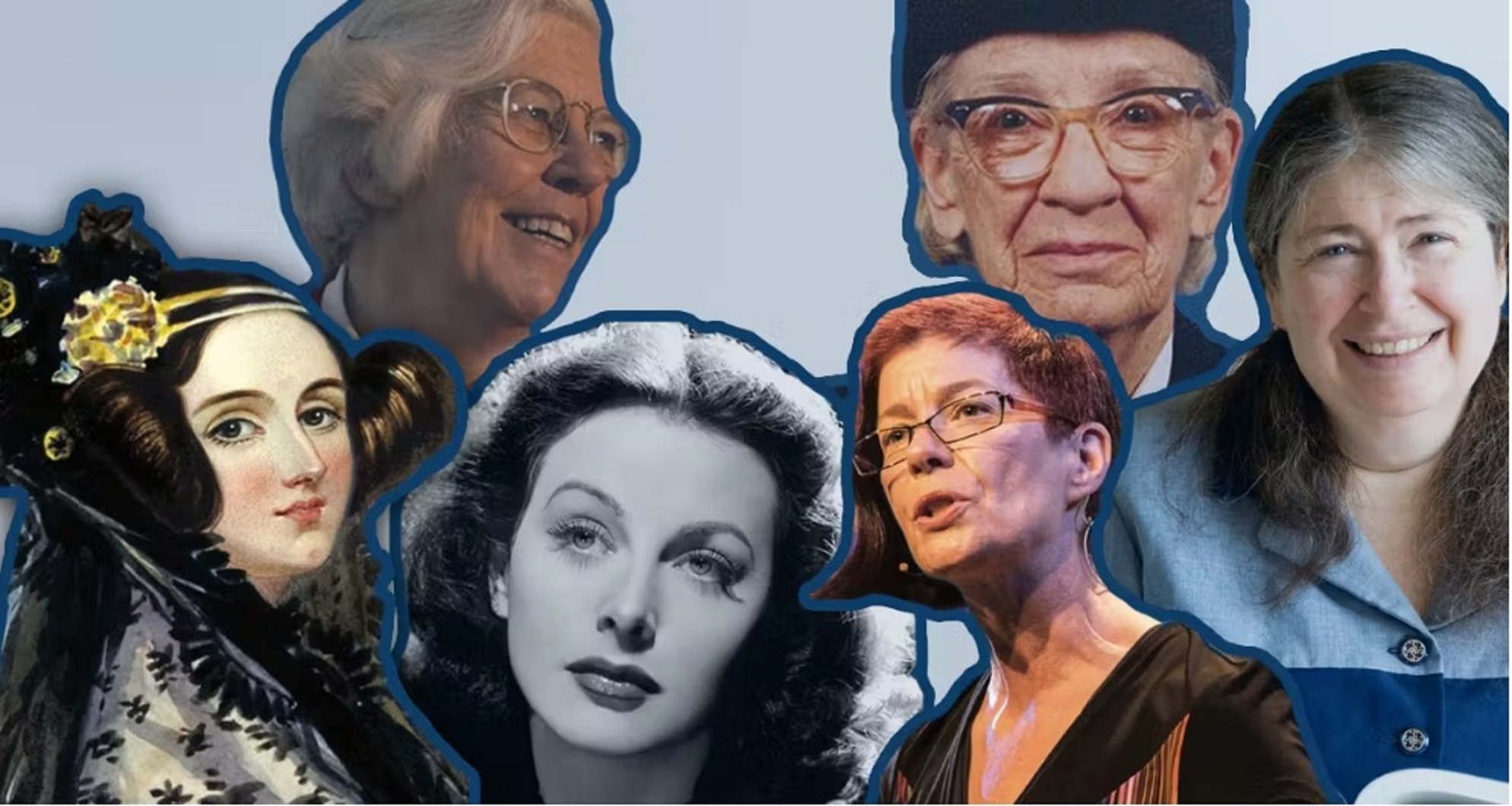
Raising awareness around individual women programmers and their specific accomplishments helps remedy the misconception that programming has always been a man’s world. On the contrary: It wasn’t always this way. Women have been paving the way since day one, so here are 16 influential female tech pioneers you need to know about.


No women created a Microsoft Exel.
Ada was not "the first known programmer"
Programming is done by 99% men with a Y chromosome and superior natural math and programming skills.
No woman "paved the way" or were around on "day one" of computer technology, other than key punch typists.
Dan Bricklin and Bob Frankston 1979 at Harvard
https://softkeys.uk/blogs/blog/who-created-excel

Baker has been widely acknowledged for her work both with Mozilla and open-source software in general. In 2005, Time magazine named her one of its 100 Most Influential People, and she’s also been inducted into the Internet Society’s Internet Hall of Fame.

The Mozilla team, led by the American developers Dave Hyatt and Blake Ross, sought to create a light fast-loading browser that would appeal to users in its efficiency.
https://www.britannica.com/technology/Firefox-Web-browser
She was a
lawyer, which is not a technical field.
Time Magazine is a leftist, girl pandering rag.

In 1987, she co-founded Systers, an online community for women to discuss the issues they experienced at work.
In 1994, she co-founded the Grace Hopper Celebration, a gathering of women technologists that’s not only still going strong but continues to grow with each passing year.
Finally, Borg created the Institute for Women and Technology, which combined her previous community-building efforts with new programs intended both to support women already working in tech and to encourage other women to enter the field. Following Borg’s death in 2003, the organization was renamed The Anita Borg Institute for Women and Technology and has since shortened its name to AnitaB.org.
So what?
What useful program did she create?

Next up: Elizabeth “Jake” Feinler, who birthed
the internet URL system we take for granted today. In 2012, Wired’s Cade
Metz wrote an excellent profile on Feinler, who, for nearly two decades, ran
the Network Information Center (InterNIC), the organization originally
responsible for overseeing the use of internet addresses and for publishing
internet directories. That’s right—before the existence of private domain
registrars and Google, one organization did it all. As part of her work at
Menlo Park, where InterNIC was based, Feinler—together with
colleagues (MEN)—famously created the top-level domain naming scheme (.com, .edu,
.org) that is now ubiquitous.
Though she is now officially retired, that hasn’t stopped Feinler from
contributing to internet advancements in the form of historical
preservation. She is an active volunteer for the Computer History Museum and
has co-compiled a timeline of the development of email. She has also donated
money, organized information, and written detailed inventories for the NIC
project archives.
In
1989, Tim Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web, using
HyperText an Internet-based hypermedia initiative for global
information sharing while at CERN, the European Particle Physics Laboratory.
He wrote the first web client and server in 1990. His specifications
of URIs, HTTP and HTML were refined as web technology spread.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tim_Berners-Lee
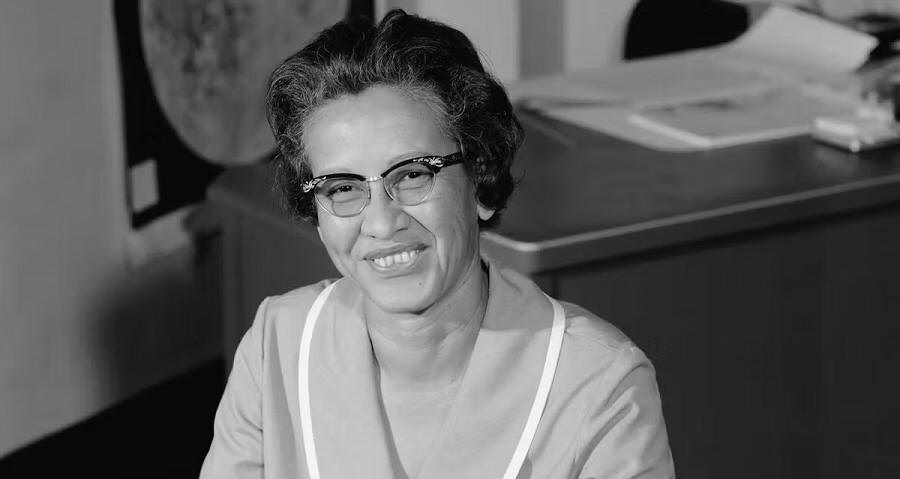

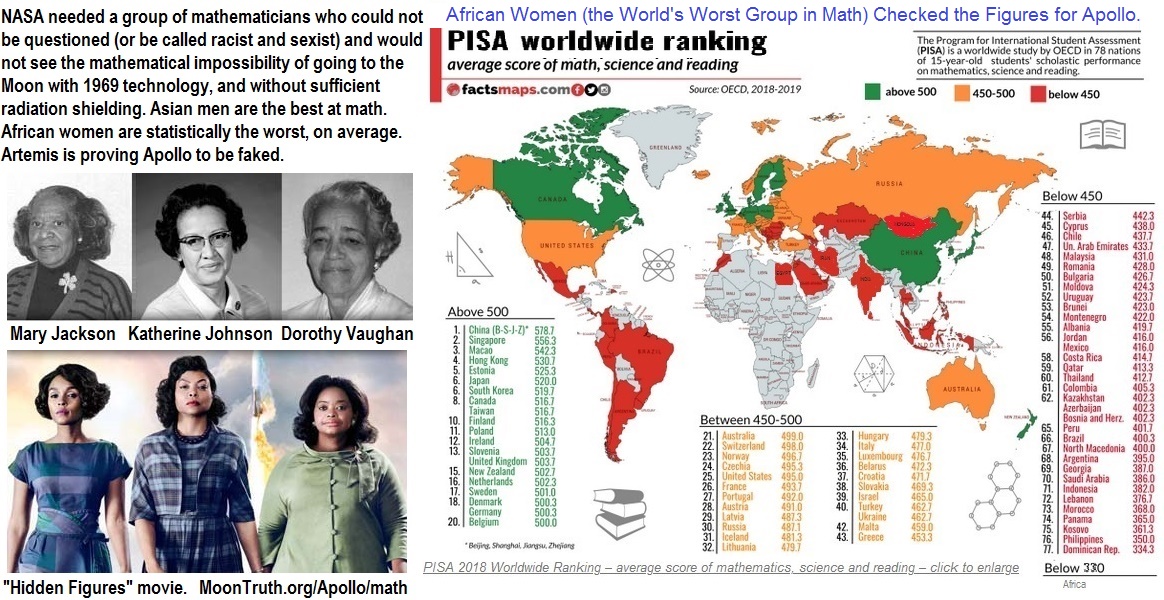
When John Glenn prepared to be the first American to orbit earth, he asked for Johnson by name to run manual tests of the computations made by computers to control the spacecraft's flight trajectory. Johnson's contributed to further space flights and reports until retiring in 1986. President Barack Obama awarded Johnson the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 2015.
www.MoonTruth.org/Apollo/math
Asian and White men mathematicians were kept away because they would quickly see the hoax.

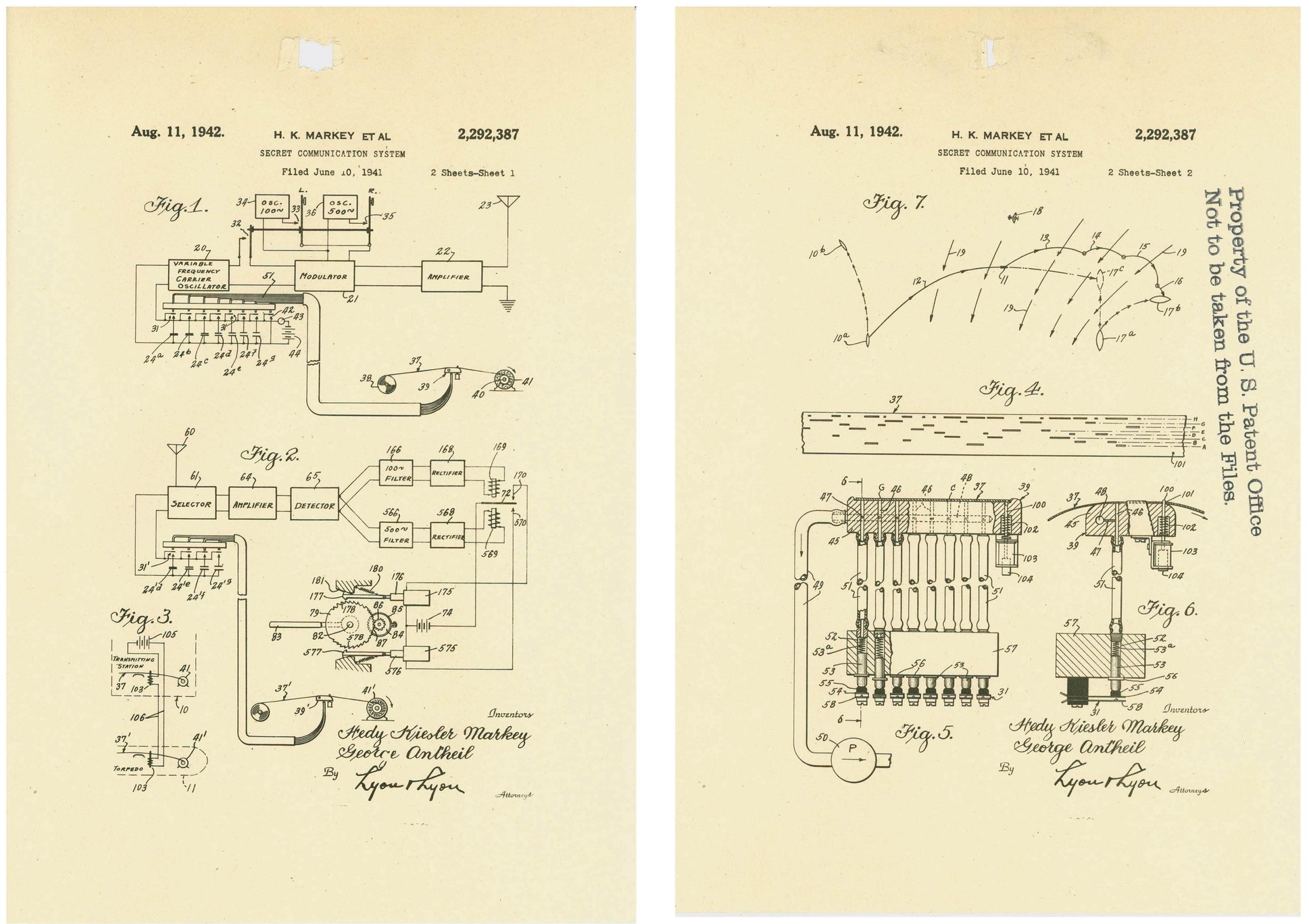
That invention, originally a radio guidance system, helped the Allies win the Second World War. That was the whole point: to use different frequencies to guide underwater missiles and render them undetectable. Sadly, despite having patented the technology—which was subsequently used by the military—Lamarr and her family have never seen a cent in return for its use during the war or in subsequent modern technologies, and you probably had no idea how this Hollywood star changed the face of technology.
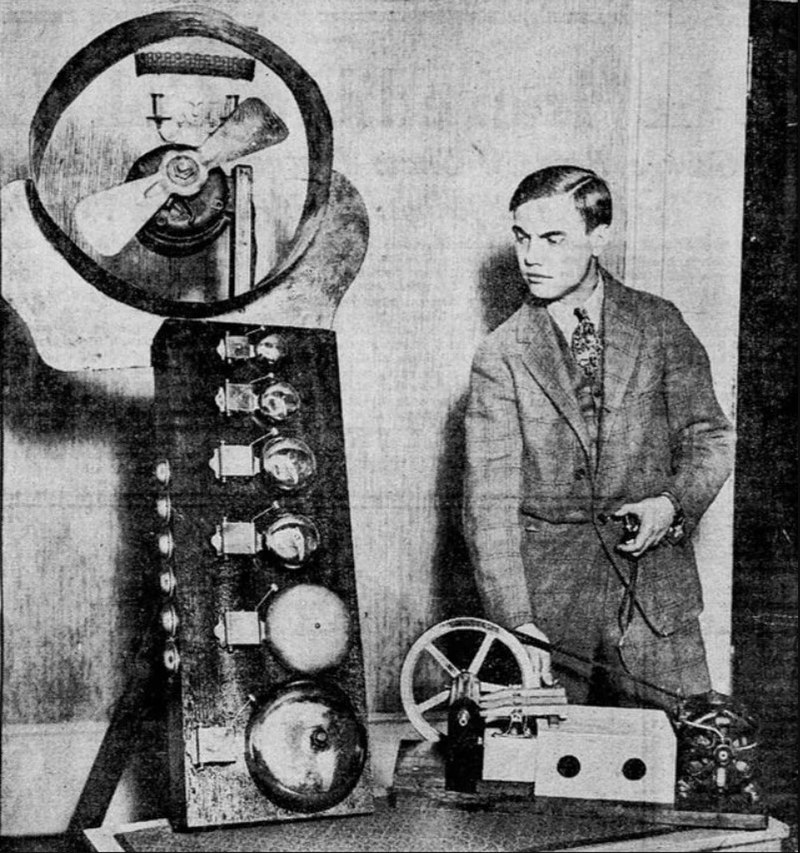

 Lamarr
assisted her boy friend, inventor George
Antheil who developed
a radio guidance system using frequency-hopping
spread spectrum technology
for Allied torpedoes
in 1941.
Lamarr
assisted her boy friend, inventor George
Antheil who developed
a radio guidance system using frequency-hopping
spread spectrum technology
for Allied torpedoes
in 1941.wikipedia.org/George_Antheil
Hedy, an actress with no science degree, had no other patents.
George was an inventor, composer, and gentleman for putting her name on his patent application to get a happy Hedy that night.
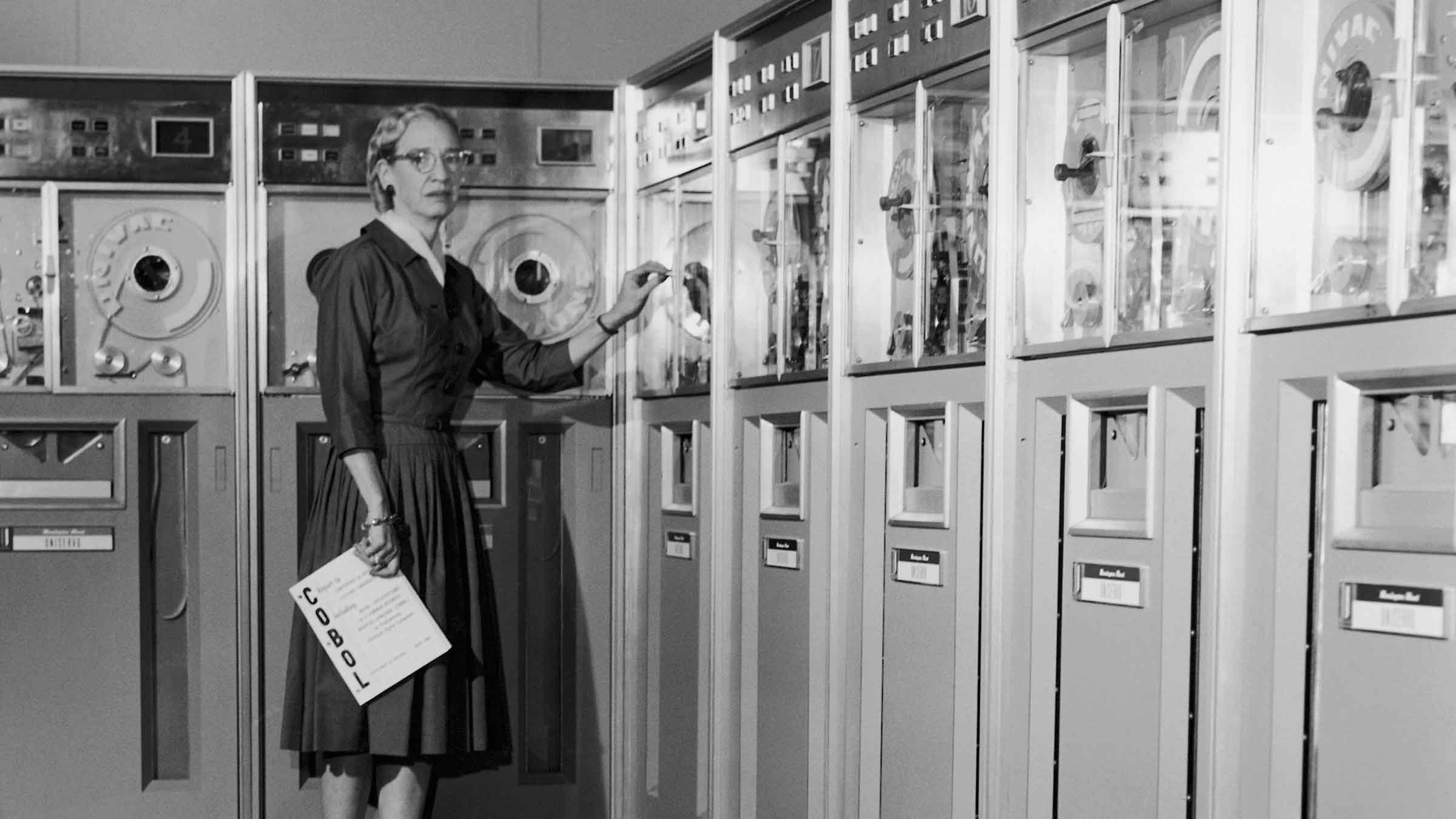


She used COBOL but did not invent it.


As a Navy WAVES lieutenant, Hopper was part of the Harvard team that built the first-ever computer, the Mark 1. After the Second World War, Hopper was involved in the creation of UNIVAC, the world’s first commercial computer. She also developed the first universal programming language for business, COBOL, which is still in use today. Hopper is even credited with coining the term “debugging.”
As Science Focus points out, her nickname “Amazing Grace” was not given without merit, and she continues to inspire women programmers today. As we mentioned, it’s for Grace Hopper that Anita Borg’s annual event for women technologists is named, and Fullstack Academy’s all-women coding bootcamp is also named for her.
She was childless.
Grace is not even at the founding meeting for COBOL.
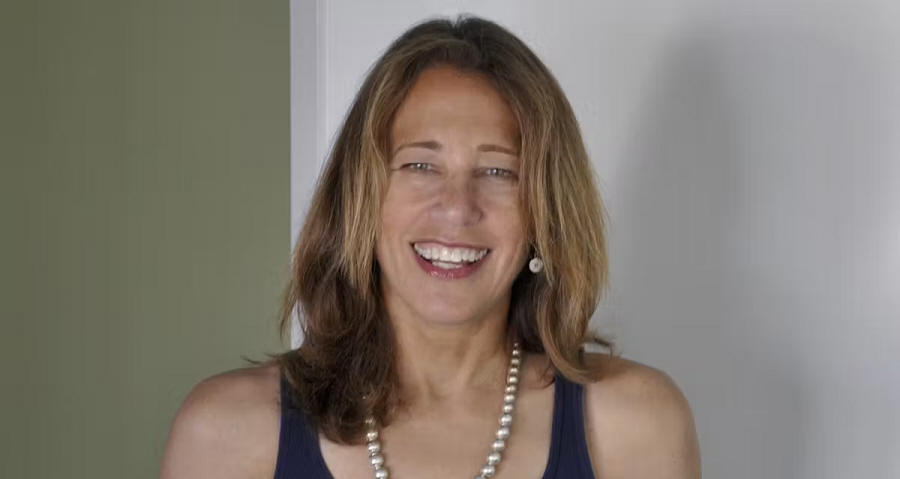


Kare was a sculptor before getting hired by Apple and pivoting into graphic design. AIGA notes that as a designer, Kare “created some of the most recognizable icons, typefaces, and graphic elements in personal computing: the command symbol (⌘), the system-failure bomb, the paintbrush, and, of course, ‘Clarus the Dogcow.’”
Since leaving Apple, Kare has started her own graphic design company, Susan Kare Design, and created logos and icons for other giants of the tech world, including Microsoft and Facebook.
So what?
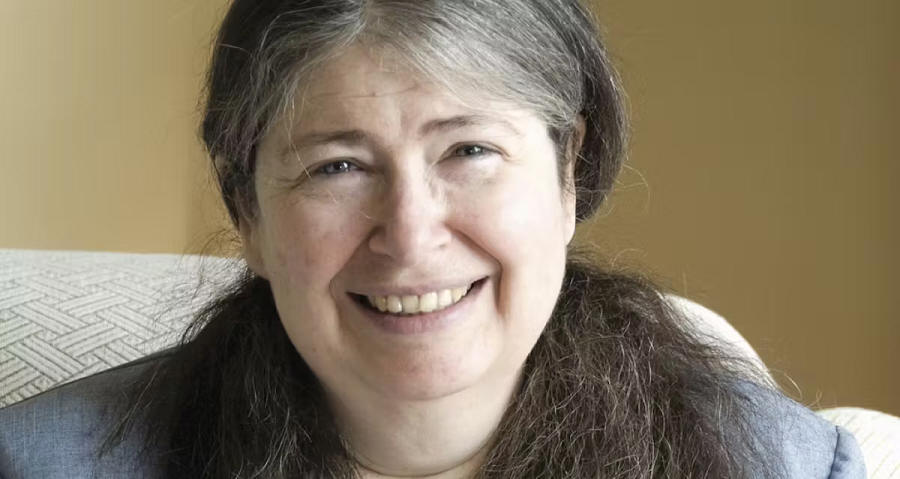

But Dr. Perlman is best known for her spanning tree algorithm, or STP for short. STP solved the initial problem of data sharing between computers and stopped data from becoming trapped in a loop. Hackaday’s Richard Baguley explains that Perlman’s solution was so simple that it now seems obvious—and yet because it was so simple, “Dr. Perlman struggled to get her fellow engineers to accept it.”
Even though Dr. Perlman’s original STP has since been updated and replaced, the fundamental idea behind it still underpins much of the internet and the related science of networking.
Sweet
So what?
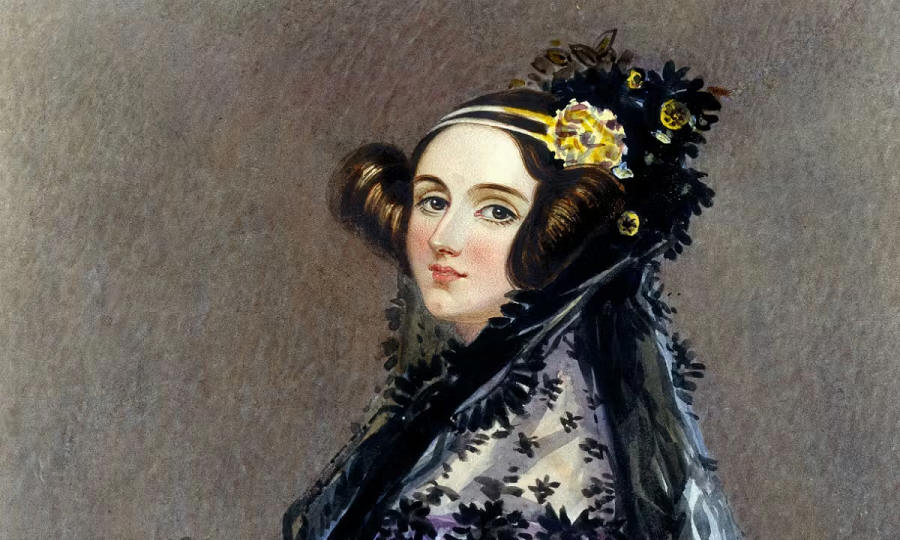

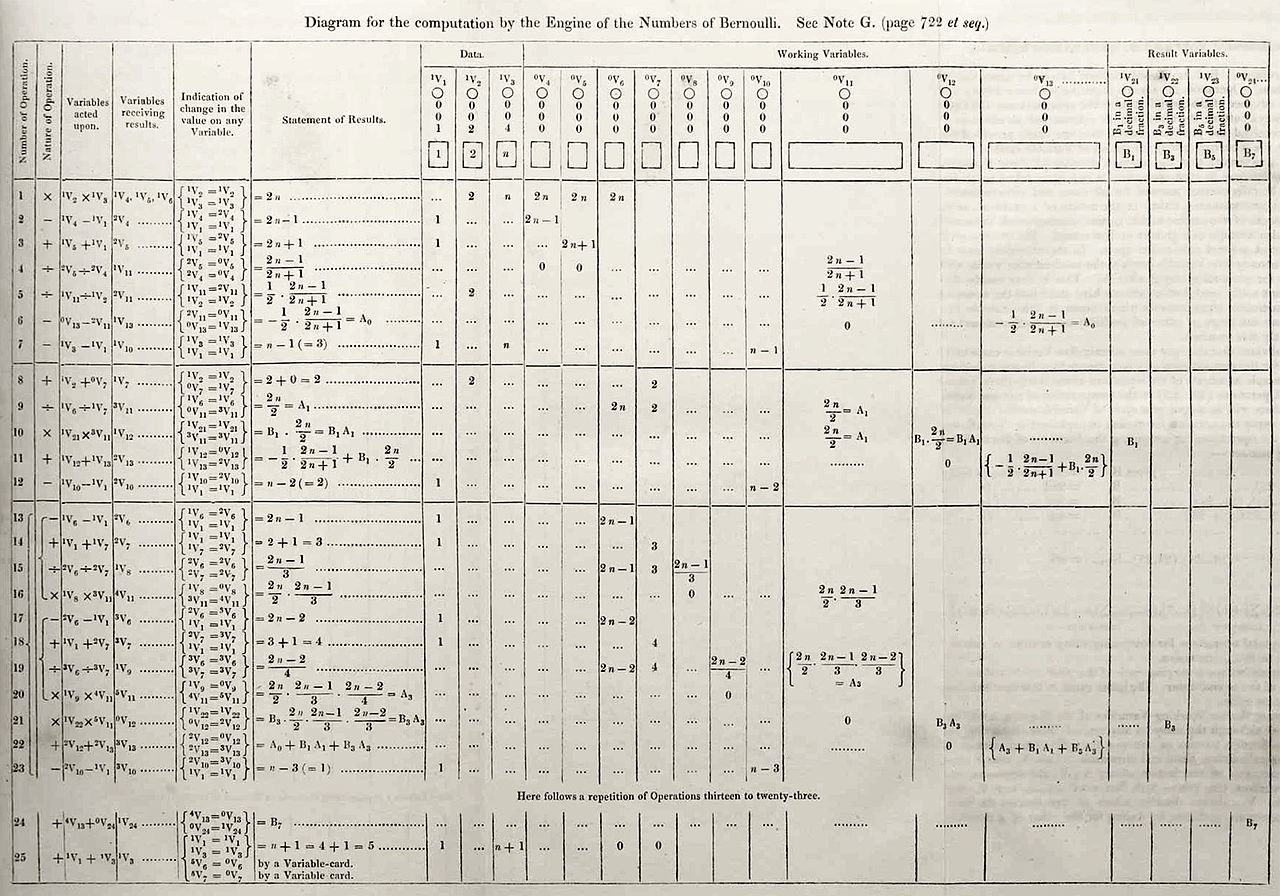
It was a program she wrote for Babbage’s computer—a program to find Bernoulli numbers, a sequence of numbers that occur frequently in number theory—that has earned Lovelace her recognition. As Two-Bit History explains, “Her program was specified with a degree of rigor that far surpassed anything that came before.” But Lovelace had an influence that went beyond her technical aptitude, says The New York Times reporter Claire Cain Miller. She was able to see the full potential of computing and understood that it could also be used to create music or art.
Lovelace’s impact on the world of technology lives on and is observed on the second Tuesday in October with Ada Lovelace Day, on which individuals and organizations alike celebrate the achievements of women in STEM.
 Charles Babbage,
English mathematician is "the father of computers" and designed the
Analytical Engine in 1836, and wrote the first algorithms and programs for
it.
Charles Babbage,
English mathematician is "the father of computers" and designed the
Analytical Engine in 1836, and wrote the first algorithms and programs for
it.
6 years later, in 1842 his friend and secretary Augusta "Ada" Byron Lovelace translated his notes, and added some thoughts about his programs. But she was obviously not the first, as some feminists claim. Her Note G is a chart, not a computer program. There were no computers to program until about 100 years later.
This is NOT a computer program.
There were no computers to run one in 1842.

Spärck Jones pioneered advances in information retrieval that empowered users to work with computers using ordinary language, rather than having to learn code. “When most scientists were trying to make people use code to talk to computers, Karen Spärck Jones taught computers to understand human language instead,” writes The New York Times’s Nellie Bowles.
But Spärck Jones is most celebrated for her 1972 paper in the Journal of Documentation, in which she introduced the concept of inverse document frequency, a method for counting the number of times a phrase appears in a document to determine the phrase’s importance. This was crucial to the subsequent development of modern search engines, which all still rely on Spärck Jones’s work today.
but there is no evidence
Larry Page and Sergey Brin
read it or used it.
They officially founded Google on
September 4, 1998 Menlo Park CA
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Google
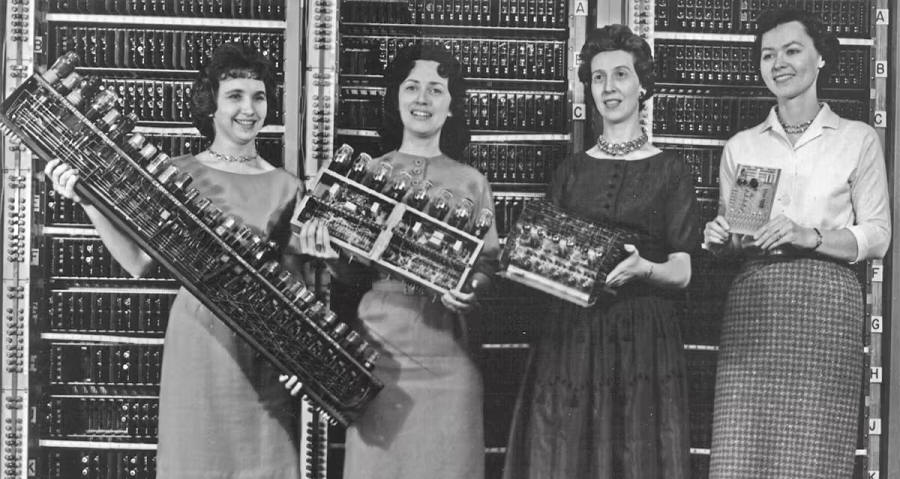

As Claire Marchand of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) explains, the women “learned to program without programming languages or tools, because none existed. They used only logical diagrams, and the work they did calculating ballistic trajectories was extremely complex. When the project was completed, ENIAC could run missile trajectories in seconds.”
Despite their pioneering work, these six women were never credited when the ENIAC was unveiled to the public in 1946. For years, they remained invisible, which is why the ENIAC Programmers Project was born to research their work, share it with the public, and honor the women who were the programmers behind ENIAC for almost two decades.
who followed instructions from men.